Initial stages
I was expected to do the following as part of the Google Summer of Code period :
-
Unsupervised learning mechanism to separate out clips with different instances of blended classical joint attention.
-
Manually annotating the clips segregated (with ELAN) and finding out different elements that would contribute to different classes of BCJA.
-
Identifying the co-speech gestures that I have planned using already known classifiers.
-
Build our own classifier using manual as well as feedback from the earlier known classifier, thus improving it altogether.
-
Testing our classifier and error correction.
-
Gesture and micro-expression detection using data-sets of highly expressive anchors as data-sets.
-
Scene continuity and change detection.
Work flow moderations
Since there are a lot of people working, there is a lot which is common across different proposals. So the work-flow changes more often than not. Thus, when the coding period began, what I needed to do to make a significant contribution to the organisation was very different that what I had proposed. Before the mid-term I was working on the Red-Hen Lab repository BlendedClassicJointAttention.
Repositories
There were two repositories that were worked upon the period.
- BlendedClassicJointAttention : Workshop of algorithms where every method implemented was present.
- BlendedClassicJointAttentionClean : A python library like structure to use the accepted algorithm implementations all at one place.
Blended Classic Joint Attention Repository
This repository deals with work done by The Distibuted Red Hen Lab towards classification of different instances of blended classic joint attention in various form of print, audio and video media. For more information visit the Red-Hen Labs
Sub-repositories
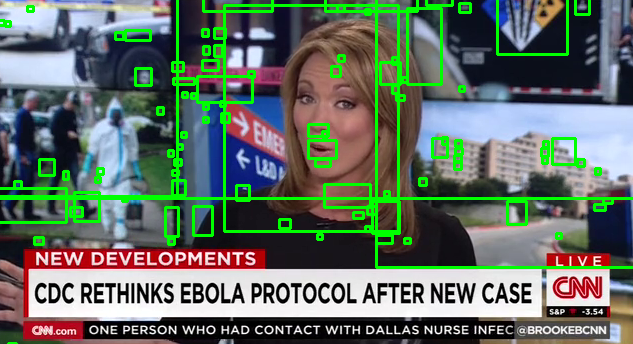
Face detection
Detection of number of human faces, possible extensions to their position and orientation. The files use Voila-Jones Haar classifier to detect human frontal and profile faces with the enhancement of template matching. The results can be seen as follows :
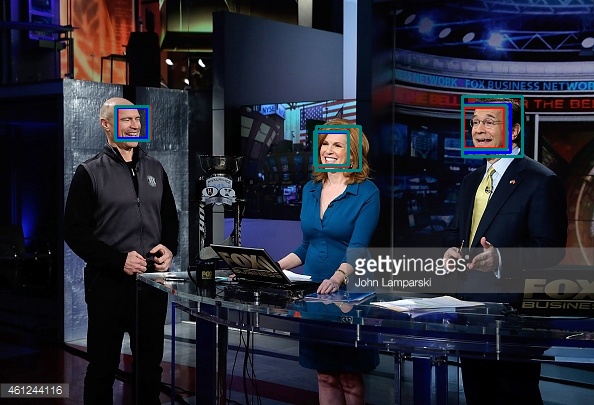

Template matching is a technique used to find a smaller image in a larger one. It works by sliding the small image accross the big one and it uses math to calculate which part of the bigger image is most likely to be the small image. This algorithm is nice because it always returns a value, unlike Haar cascades which is returns a position only if it finds a face.
Emotion recognition
Recognising different emotions (sad, happy, surprised, neutral etc.) using a CNN classifier. To see and example run :
python webcam-emotions.py --displayWebcam --seeFaces --netFile soumitra.p
To get best results (and tailored for the person who is using the webcam app), you can use the webcam-emotions.py script to record data, as follows,(train happy by replacing sad by happy):
python webcam-emotions.py --displayWebcam --seeFaces --gather_training_data --recording_emotion sad
Gaze direction recognition
Calculating angle of ones gaze using initial pupil detection and terminal points of eyes. The algorithm used was from the paper which deals with prediction of centre of the eye via gradients.
The step-wise procedure is as follows :
- Extraction of eyes from the face, via
Voila-JonesHaar classifier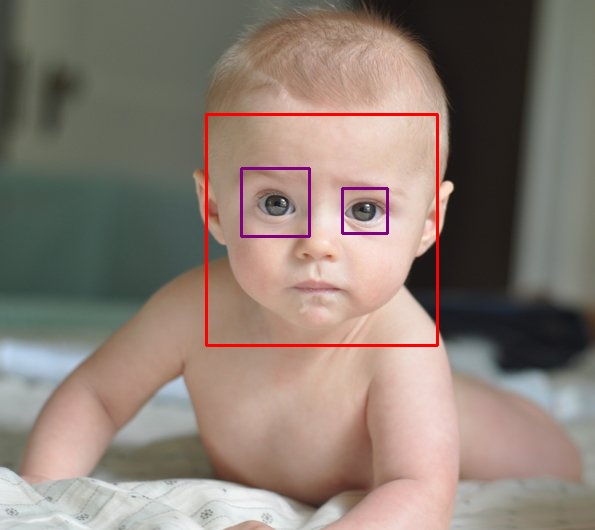
- Extracting and thresholding the area near the eyes so that the dark part is apparent
- Detection of blobs in the specified area
- Finding centre of the blob via the algorithms



Several other algorithms, including use of hough circles are present in bin which were descarded as second to the upgiven.
Context recognition
Recognising what context is a specific scene in using Lucas-Kanade, optical flow. The following were the outputs in accordance to the used algorithms
-
Good features to track

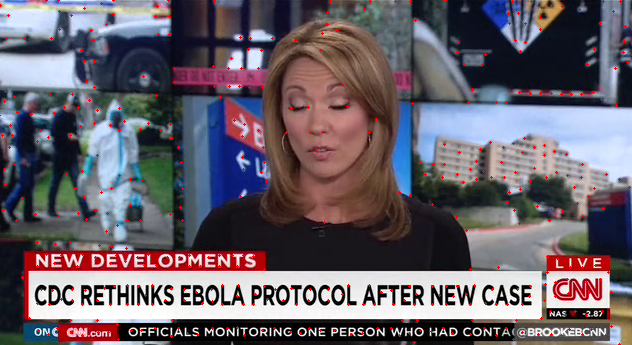
-
Lucas-Kanade
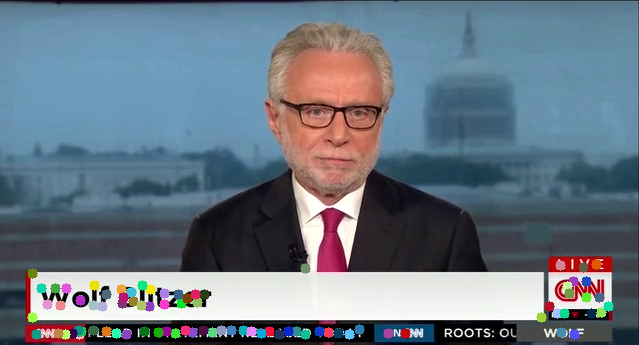
-
Optical flow

Scene continuity
Detection of a scene change by creating an average image at every new scene and calculating the difference with the newly observed. The following image would give a better insight into how the threshold and mean images were compared

The upgiven image was how the threshold changes at different instances with it being re-initialised once a new frame is detected. The following image is a pictorial representation of how much an image differs from another.
If this difference crosses a certain threshold, scene change is reported.
Facial Landmark detection
Detecting major facial landmarks, which is useful for Gaze direction and Emotion recognition. Pre-built python library Dlib was used to create a mat of human facial features, with a little tweaking. The outputs are as follows
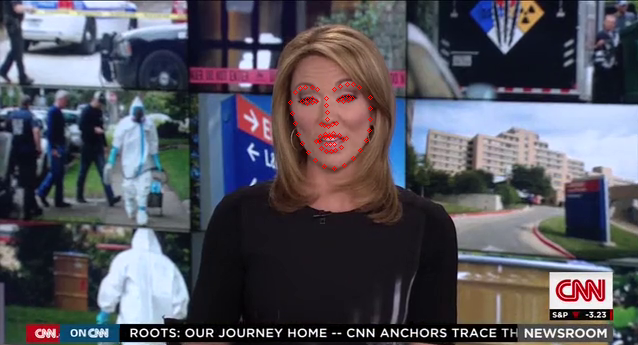
Head pose
Configuiring head pose to gaze direction and independent head pose estimation, via the features tracked in the Facial landmark repository.

Gesture Recognition
Recognising multimodal gestures. Since this required parsing through ELAN files and reading EAF for different gesture signals combined with video.
Posture Recognition
Body posture recognition was worked upon using flowing puppets and Histogram of gradients. Something like the walking posture can be seen here

Window Size
The size and number of different windows is the giveaway clue to predicting whether Blended Classical Joint Attention exxists or not. Thus contour detection and shape matching techniques were used to predict the number of rectngular shapes.

Reaction Shots
Analyse reaction shots (of surprise, awe etc.)
Blended joint attention clean
A python library like structure to use the accepted algorithm implementations all at one place. Which looks something like this :
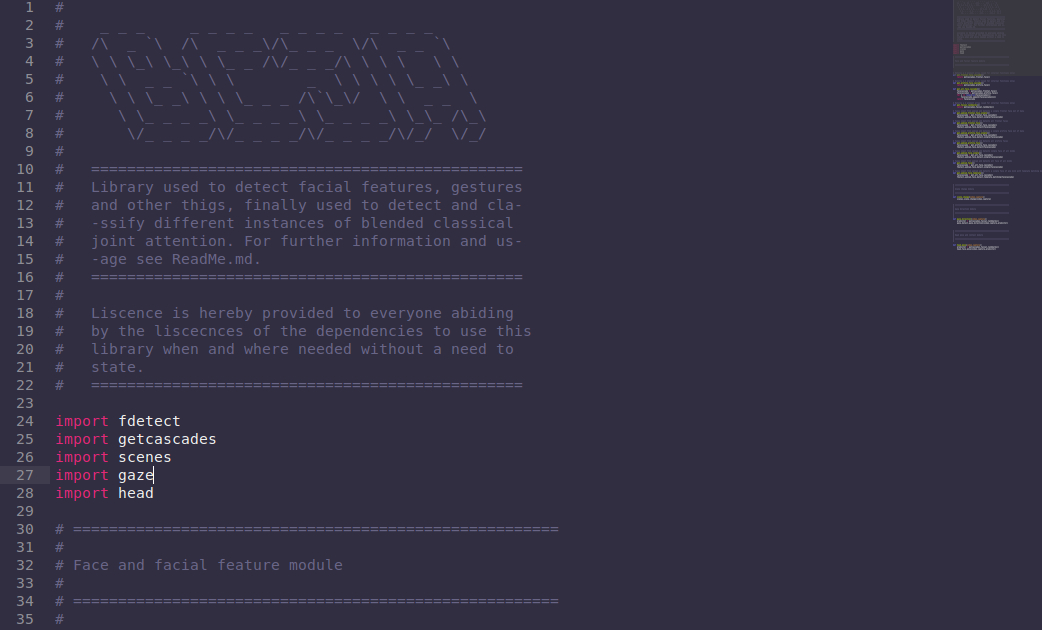
The repository can be looked upon here. The accepted algorithms were placed on the Case High performance computing cluster.
Required Packages:
- Python 2.7.x
- Numpy
- Bob
- Matplotlib
- OpenCV (One must check compatibility with python and OS)
- DLib
- pympi-ling
- PySceneDetect
- Read
Authors:
- Dr.Mark Turner
- Dr.Francis Steen
- Soumitra Agarwal

- Debayan Das
